Defining Linguistic
Terms
For the variables identified above, we define
the allowed values:
Light { low, high }
Electric Voltage { low, high }
This set defines the terms for Light as low
light or high light. Note that in normal circumstances
there would be a middle state between low and high light densities.
However, for the sake of simplicity this example only shows these
two states.
Define the Fuzzy Knowledge Base
Once defined, the linguistic variables are the
building blocks for constructing the rules of a fuzzy
knowledge base. For Example:
| Rule1 |
| |
IF light = "high" |
| |
|
THEN electric voltage = "low" |
| Rule2 |
| |
IF light = “low” |
| |
|
THEN electric voltage = “high” |
In summary, if the amount of natural light is
low then the voltage to the bulb is high. However,
if the amount of natural light is high then the voltage is low.
Defining the Fuzzy Sets for the Linguistic Terms
Two fuzzy sets for the linguistic variable
light are now defined, one for low and the other for
high. We also define two fuzzy sets for the electric voltage. These
become the fuzzy linguistic sets. Please note that these values are
quite arbitrary.
Low_light = { 0/5, 1/10, 0/15 }
High_light = { 0/10, 1/15, 0/20 }
Low_voltage = { 0/12, 1/14, 0/16 }
High_voltage = { 0/14, 1/16, 0/18 }
I employed the simple technique of human
intuition to define the values for the fuzzy sets i.e.
for fuzzification. However, there are other advanced techniques, such
as Genetic Algorithms, Neural Networks, and Angular Fuzzy Sets, which
are separate subjects of study on their own.
The key difference between a normal set and
a fuzzy set is that either the normal set values are
members of the set or they are not. In the fuzzy set, they belong
to the set with a membership function. Another way to look at it as
a percentage of membership.
Given the fuzzy sets defined above, we
examine the Low_light fuzzy linguistic set. The value
5 matches the right side of "0/5" so it returns a membership
value of 0. The value 10 returns a |
|
 |
|
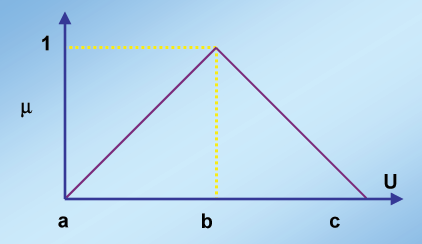
Figure 1: Definition of Low_Light where
a, b and c are the values of the fuzzy sets and u is the input
crisp value. For the fuzzy set ‘Low_Light’ the values
would be a = 5, b= 10 and c=15
|
 |
|
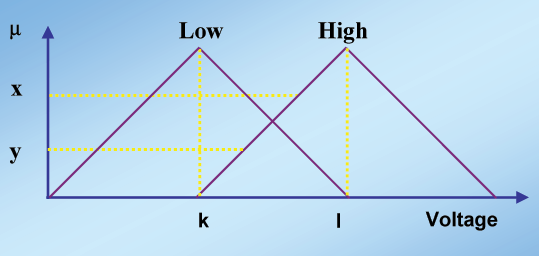
Figure 2: The calculation of the membership
set for Low_Light and High_Light.
|
 |
|
Figure 3: Defuzzification - Mapping of the
membership values of the light set onto the voltage set
|
membership value of 1 while the value 15 has a membership
value of 0. Therefore, since the value 10 is the ideal low light,
when that is a room's light density, we consider it the perfect low
light level.
In this example, only three membership values are
defined
for three representative values. This is typical of the manner in
which we think -- two extremes and a value in the middle. For example,
people traditionally think of middle age as:
- 35 - low boundary for middle age
45 - correct middle age
50 - upper boundary for middle age
Using this definition, anyone between 35 and 50
may be
considered as middle aged, but a person aged 45 is the ideal, typical
middle-aged person.
|