|
respond to the words 'low' and 'high' - how do we
supply the output? That is where Defuzzification finishes the process.
Defuzzification
From the previous step we have 'x' and 'y';
the input value belongs to low_light set to the degree
of 'x' and to the high_light set to the degree of 'y'. These x and
y values must be mapped on to the voltage fuzzy set - on the low and
high voltage fuzzy linguistic sets. The output membership function
values are:
m low_voltage(u) = y
m high_voltage(u) = x
Now we use the Weighted Average Method to
arrive at the crisp value. (A Weighted Average Method
starts with a sequence of function values and a matching sequence
of real numbers, called weights, where the sum total of all weights
is one. The sum of all products of the weights times the function
values is defined as the function values weighted average.) Please
note that I choose this method for simplicity but there are other
sophisticated methods that are mathematically rigorous (See Ross -
1995).
Z* = 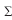 mC(`Z
) .`Z / mC(`Z
) .`Z / 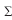 mC(`Z
) mC(`Z
)
(Ross, 1995)
Z* = x . l + y . k / (x + y)
So the Z* will be the crisp value given as the
output to the fuzzy energy saving bulb.
An Example
Assuming the fuzzy sets defined above, we try
the system with a crisp value of 11. First, convert
the fuzzy value to a crisp value.
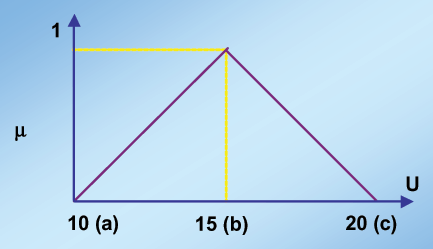
Since u (11) falls in between 'b' i.e. Since u(11)
falls in between 'b' i.e. 10 and 'c' i.e. 15 (see Fig
4) for the low_light fuzzy set we use:
(c-u) / (c-b) for b<= u <= c
(15-11) / (15-10) = 0.8
Since u (11) falls in between 'a' i.e. 10 and 'b'
i.e. 15 (see Fig 4) for the high_light fuzzy set we
use:
(u-a) / (b-a) for a <= u <= b
11-10 / 15-10 = 0.2
|
|
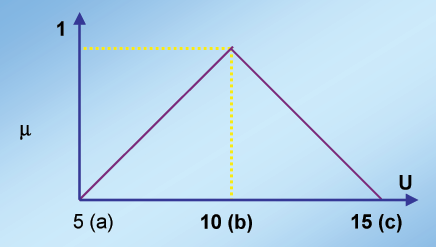 |
| Figure 4: Low Light Fuzzy Set |
 |
| Figure 5: High Light Fuzzy Set |
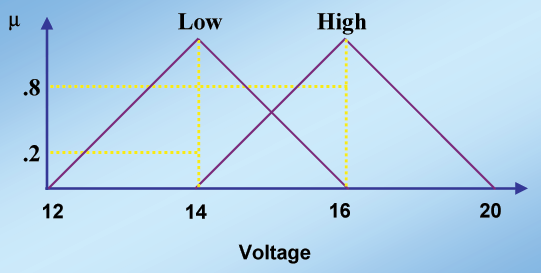 |
| Figure 6: Defuzzification in the Example- mapping of the membership
values ofthe light set onto the voltage set |
Therefore, the input crisp value belongs to the low
light and the high light sets with the membership 0.8 and 0.2 respectively.
Consulting the Fuzzy Knowledge base, we realize that the voltages
must be low and high. For the low light membership, the voltage must
be high to the degree of 0.8. For the high light membership, the voltage
must be low to the degree of 0.2. We project the membership values
of the low and high light on to the low and high voltage sets (See
Fig 6). |