|
|
Fires start out as hot spots in areas
that were probably not hot before.
When we extend the sensory
systems to include off the shelf infrared and smoke detection systems,
in addition to intruder detection, it is possible to perform fire
detection - possibly before there are flames. As the robot makes its
rounds, it notes changes in its environment and if it detects a hot
spot, the robot immediately brings it to the attention of the guards.
If the robot detects smoke from a new hot spot, then a fire is probably
imminent.
Immediately the robot can notify
the appropriate parties via wireless communications that a fire has
broken out or is imminent. While fire fighting support is on the way,
the robot could, with an onboard fire extinguisher, discharge its
entire reserve in an attempt to either extinguish the fire or slow
its advance.
In the post 9/11 world, the addition
of bomb sniffing equipment to patrolling mobile robots may be an important
augmentation in our focused efforts to prevent terrorist attacks.
The Near Term Opportunity for Traditional AI
Implementations
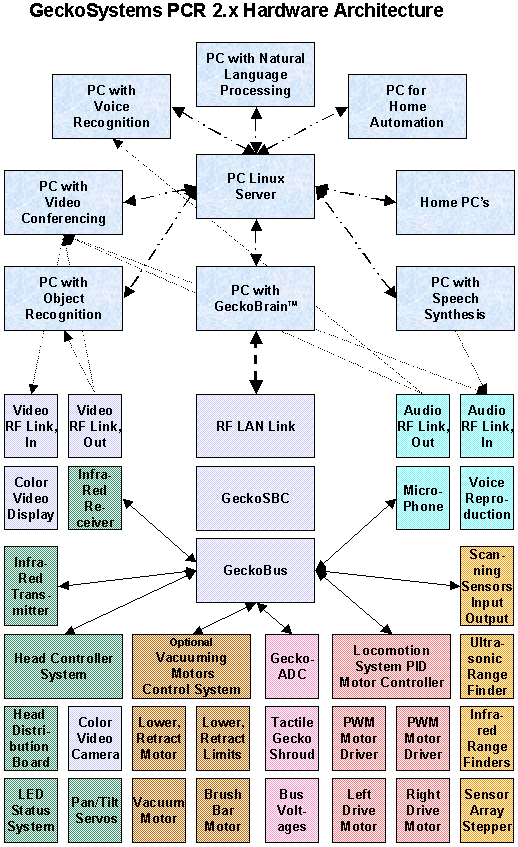
The flow chart in figure 1 illustrates
the global view of this confluence of technologies in robotics, and
specifically mobile robotic solutions. It is clear that most, contemporary
AI technologies such as expert systems, neural nets, natural language
processing, object recognition, machine vision, AI personalities,
speech recognition, speech synthesis and problem solving need to be
part of this behavioral processing center.
Just as Mr. Brooks and his
esteemed colleagues have witnessed emergent behaviors in their research,
GeckoSystems has seen that behavior in their automatic self-navigation
AI software development and usage. Emergent behavior is behavior seen
that was not initially programmed into the system. For example, the
moving to the left and then right when encountering a dynamic obstacle
that also moves to the |